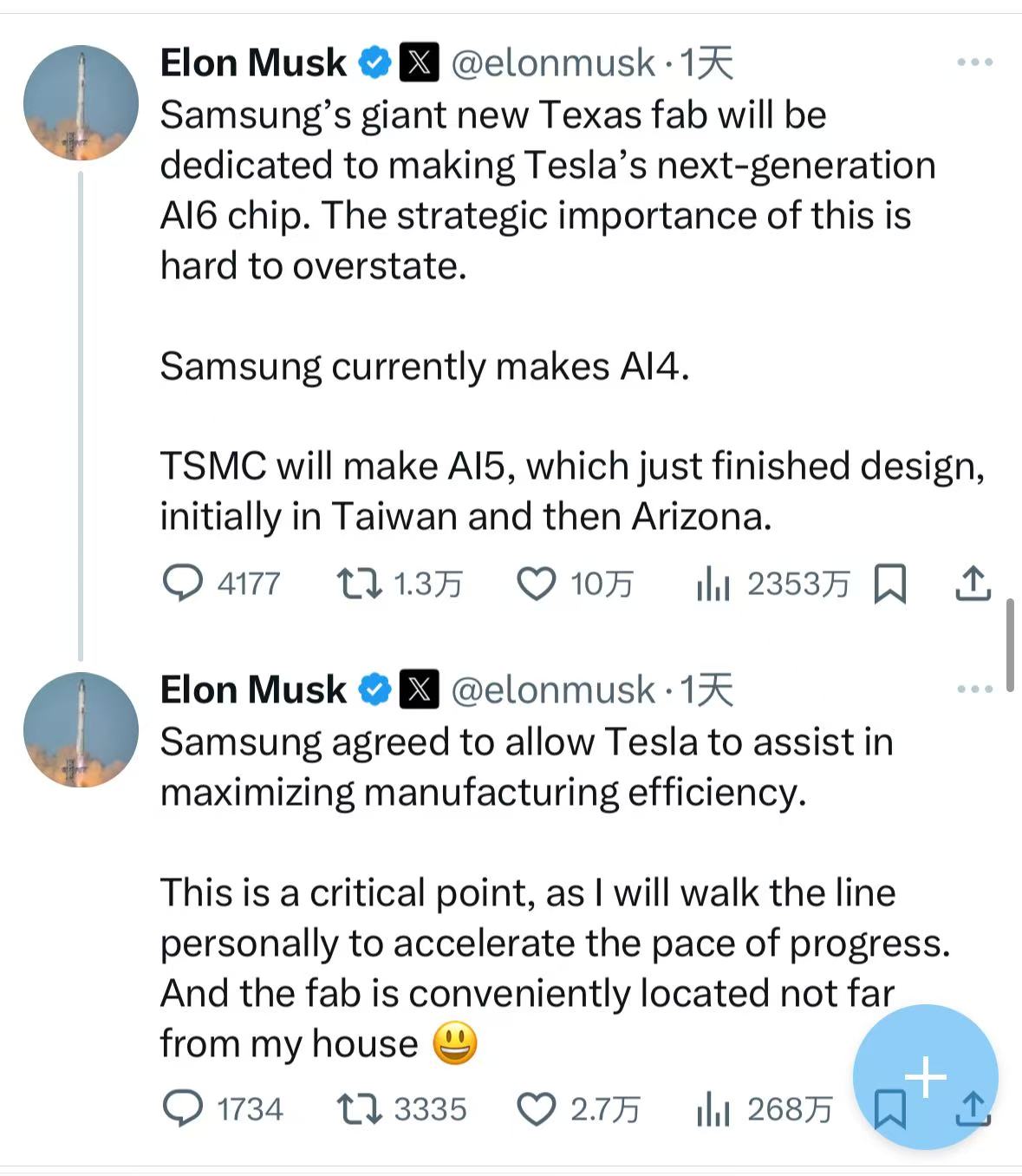
Recently, it was reported that Samsung Electronics will produce semiconductors for Tesla under a new $16.5 billion agreement, which is expected to boost its underperforming foundry business. Specifically, Samsung Electronics announced a chip production agreement worth 22.8 trillion won with a client, set to last until the end of 2033. According to an anonymous insider, Tesla is that client, and the company has already been in business with Samsung's chip foundry division. Following this news, Samsung's stock rose by 3.5% in Seoul, marking its largest intraday gain in nearly four weeks. Elon Musk later confirmed the report on X, stating that 'Samsung's factory in Texas will produce Tesla's next-generation AI6 chip, while Samsung is currently producing the AI4 chip,' and added that 'TSMC will first produce the newly designed AI5 chip in Taiwan and then in Arizona.' Samsung not only produces memory chips in-house but also offers foundry services to clients. However, its market share in chip production has been declining, struggling to secure enough orders to fully utilize its foundry capacity. The acquisition of a significant order from Tesla is expected to greatly invigorate Samsung's foundry business. As a major player in the global semiconductor field, Samsung's business spans memory chips, foundry services, and displays. In the foundry sector, Samsung is the second-largest foundry manufacturer in the world, just behind TSMC. However, its foundry business has faced challenges in recent years, with analysts noting that external expectations for its profitability have been low due to sluggish foundry order volumes alongside difficulties in keeping pace with AI demand in its memory business. Over the past year, Samsung's stock has declined by 16.44%. According to market research firm TrendForce, TSMC holds the top position among the world's top ten wafer foundries with a market share of 67.6%, thanks to its speed in implementing advanced processes and yield control. Meanwhile, China's SMIC is rapidly catching up with Samsung, with its market share rising to 6% and continuing to grow. Samsung's revenue for Q1 2025 saw a significant decline of 11.3%, dropping to $2.893 billion, with its market share falling from 8.1% to 7.7%. Analysts have indicated that Samsung is struggling with key clients turning to TSMC for advanced chips, with tech giants like Apple, Nvidia, and Qualcomm now among TSMC's clients. In this context, the $16.5 billion foundry order from Tesla is undoubtedly a much-needed boost for Samsung. Analyst Pak Yuak from Kiwoom Securities stated that this latest deal will help reduce losses in Samsung's foundry business, estimating that losses for the first half of the year will exceed 50 trillion won (approximately $36.3 billion). New Korea Investment Securities analyst Ryu Young-ho believes that while this contract may not significantly impact annual foundry revenue, its long-term significance as a catalyst for technological improvements and innovation is substantial. Notably, renowned analyst Ming-Chi Kuo indicated that Tesla plans to mass-produce the AI6 chip by 2027, utilizing Samsung's 2nm (SF2) advanced process. The current yield for SF2 is 40-50%, lower than TSMC's N2 process yield of over 70% and Intel's 50-55%. While SF2 employs GAA (gate-all-around) technology beneficial for mass production, predicting whether the AI6 chip can be produced on schedule remains difficult. Nevertheless, following this news, Samsung's stocks in Seoul surged 6.8%, reaching the highest level since last September, while its suppliers such as Soulbrain saw stock increases of up to 16%. Meanwhile, Tesla's shares rose in pre-market trading by 1%. For Tesla, entering into a foundry agreement with Samsung is a crucial step in its chip strategy. Tesla has been committed to the development of autonomous driving technology, with chips being a core component for achieving this. Currently, Tesla's Full Self-Driving (FSD) system relies on chips for its computational power. As mentioned earlier, according to Musk, Samsung's factory in Texas will produce Tesla's next-generation AI6 chip, while the intermediate AI5 chip will be manufactured by TSMC, first in Taiwan and then in Arizona. Tesla's choice to collaborate with Samsung is partly due to its diversification strategy for its supply chain. Historically, Tesla has not relied on a single supplier for chip sourcing. By working with various foundry manufacturers like Samsung and TSMC, Tesla can mitigate supply risks due to issues with any one supplier, ensuring stability in chip supplies. Additionally, Samsung possesses deep technical expertise and large-scale production capabilities in semiconductor manufacturing. Although it trails TSMC in certain aspects of advanced processes, Samsung remains strong in chip manufacturing technology, and its plant in Texas aligns with Tesla's strategy for supply chain localization. Musk indicated that Samsung has agreed to work with Tesla to maximize production efficiency, with his personal involvement to accelerate progress, reflecting Tesla's emphasis on collaborating with Samsung for AI6 chip production. Overall, the foundry agreement between Samsung and Tesla holds significant implications for both parties and the entire semiconductor foundry industry. The future developments of this agreement, including the production progress of the AI6 chip, the potential turnaround of Samsung's foundry business, and the evolution of the competitive landscape in the industry, will need time to unfold.
Samsung to Manufacture Semiconductors for Tesla in $16.5 Billion Deal
Share this post on: