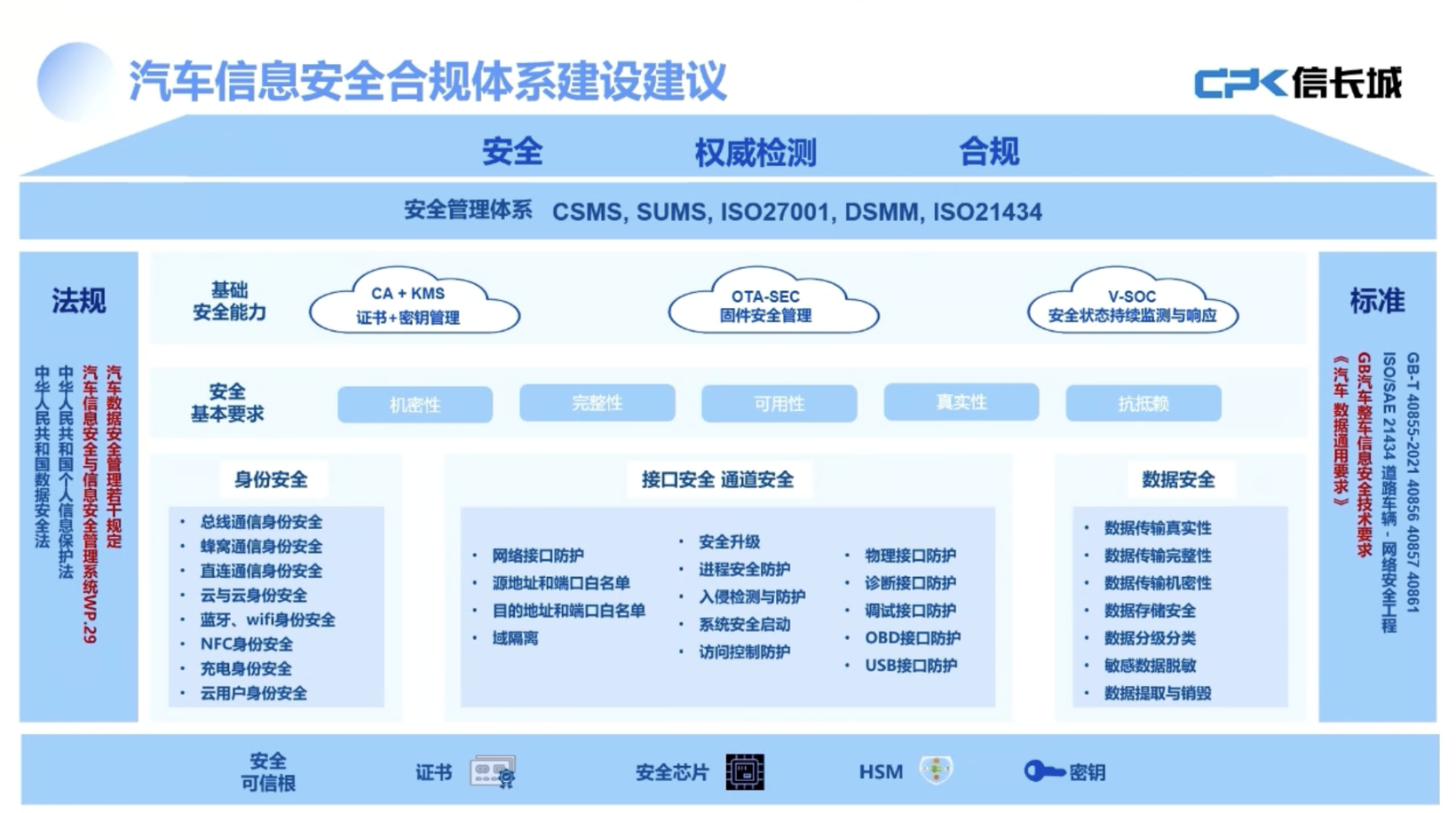
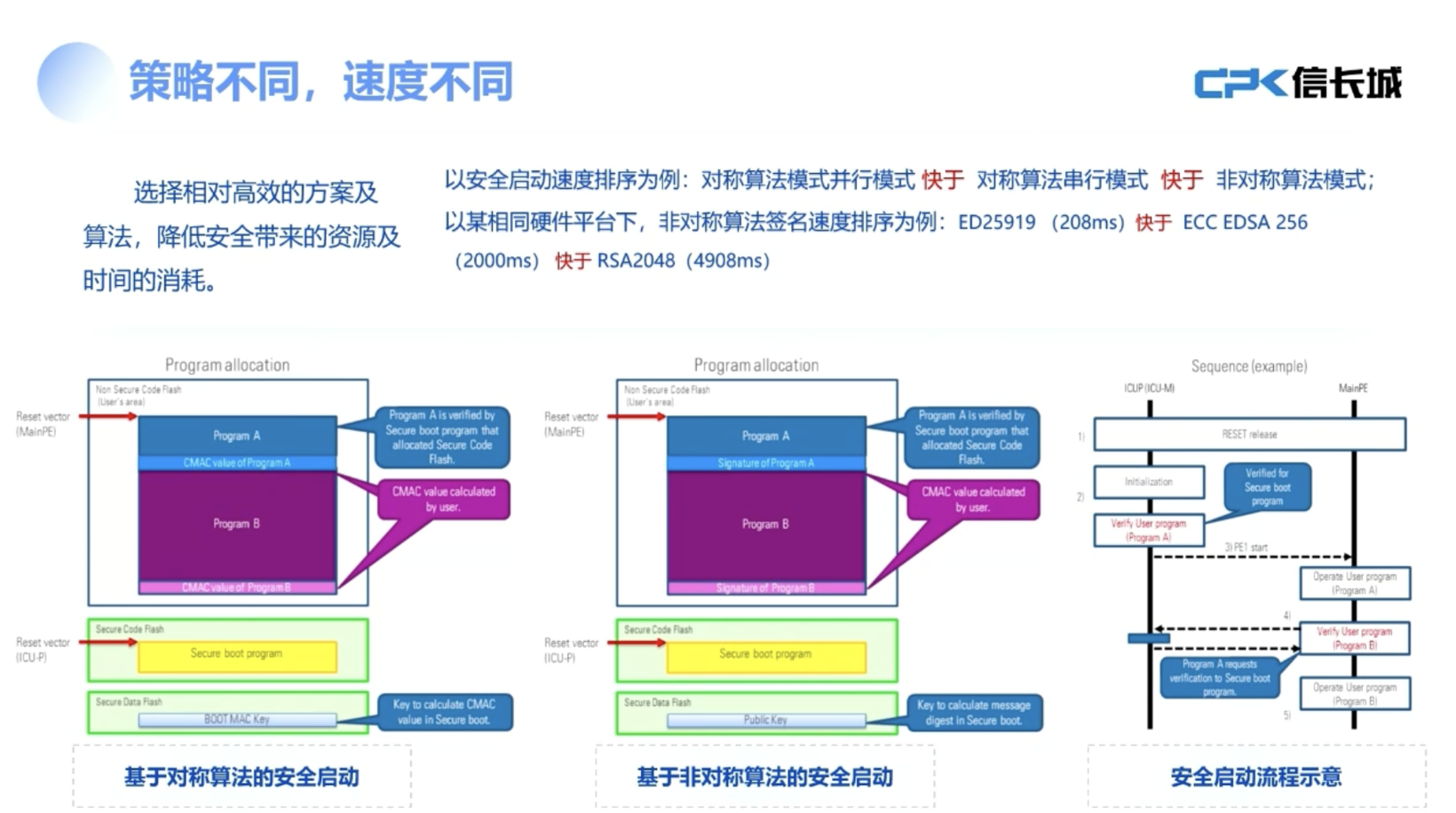
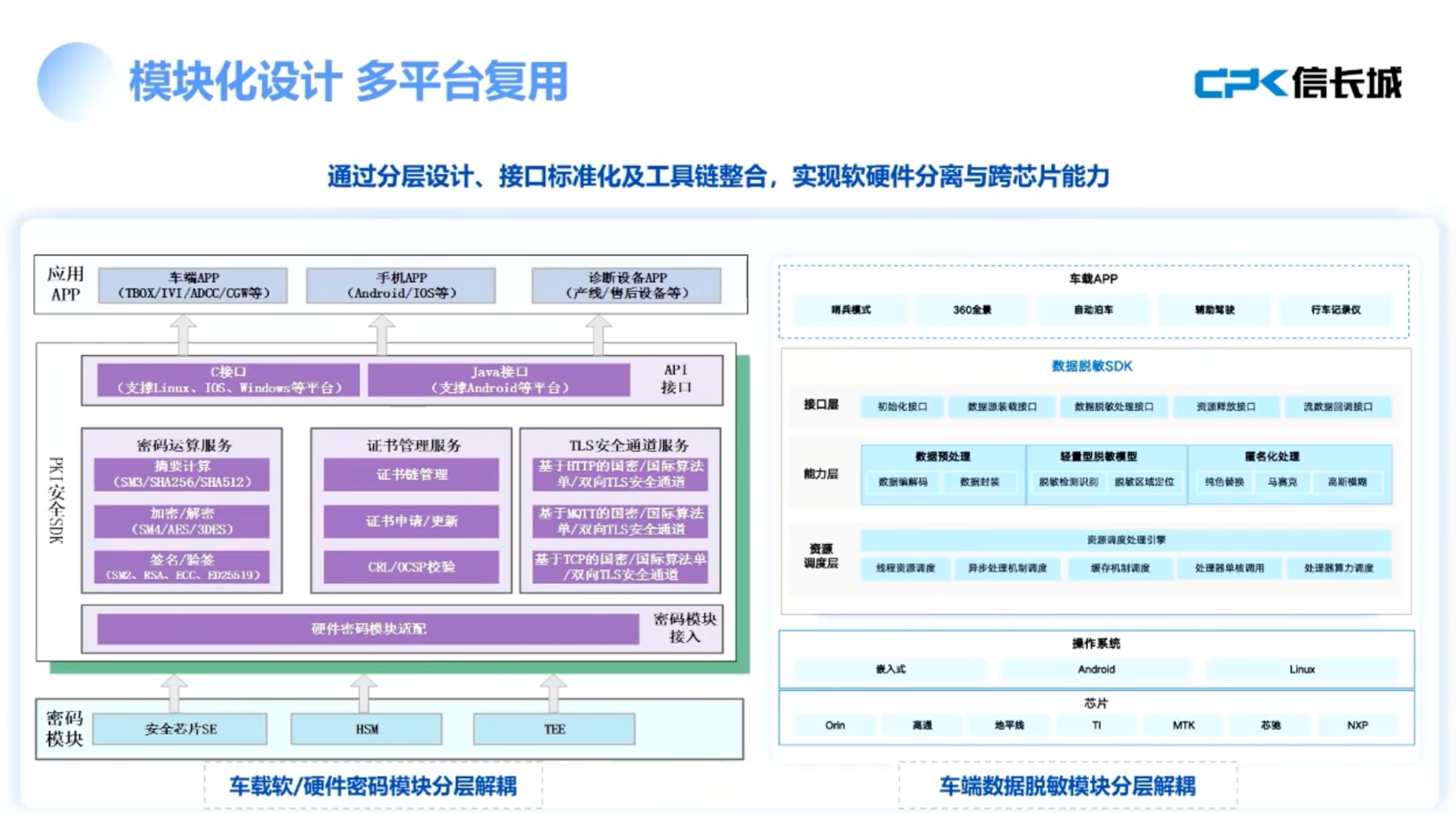
On June 19, 2025, at the Fourth China Internet of Vehicles Security Conference, Liu Peng, co-founder and CTO of Beijing Xinchangcheng Technology Development Co., Ltd., pointed out that the automotive information security field faces multiple risks and requires a comprehensive security system that encompasses both technical and management levels. He emphasized the importance of cryptographic technology in whole vehicle-level security protection and proposed implementing secure startup and upgrade measures at the component level to address security threats from remote control commands. Liu mentioned that domestic companies are actively promoting the commercial password transformation process to meet relevant standards. While ensuring security, Liu also explored how to enhance user experience. He recommended using hardware acceleration solutions, such as integrating independent Secure Element (SE) or utilizing the Hardware Security Module (HSM) embedded in the Electronic Control Unit (ECU), to optimize the processing speed of encryption algorithms. Furthermore, he proposed various strategies to improve overall processing efficiency, including optimizing model efficiency, refining the design of preprocessing and post-processing stages, and fine-tuning based on the continuity characteristics of video sequences to reduce resource consumption and enhance processing speed. Liu's speech highlighted that the automotive information security domain is increasingly complex compared to traditional IT fields, due to widespread risks from external wireless networks, wired interfaces, cloud platforms, and more. As vehicle-road collaboration and vehicle-cloud integration develop, vehicles may also face security threats from road infrastructure and charging piles. He suggested constructing a robust security system where both technology and management play crucial roles, emphasizing that '30% is technology and 70% is management.' From a technical perspective, he recommended establishing a certificate and key management system on the platform level, ensuring OTA security, and building a Vehicle Security Operations Center (V-SOC) management platform. On the bottom layer, hardware or software cryptographic modules should be equipped to protect core keys and critical unmodifiable configuration data. Liu also emphasized the need for secure communication between components, between components and external devices, and between components and the cloud, focusing on identity authentication and data security issues. For core components with upgrade capabilities, secure startup mechanisms and access control strategies should be implemented. Liu proposed that to ensure the security of remote control commands, various measures should be taken at the application layer, particularly to prevent command tampering, advocating for end-to-end security protection. He detailed that mobile devices send remote control commands, which should be verified by the cloud without excessive operations that could introduce new security vulnerabilities. Meanwhile, the cloud should perform a secondary signing to ensure command safety throughout the transmission process. Liu also discussed the need for infrastructure on the platform end, including building certificate management systems, key management systems, V-SOC platforms, and OTA security management platforms. He noted that while domestic companies are pushing for the formulation of mandatory standards related to automotive cryptographic application technology requirements, many have demonstrated a strong willingness to proceed with commercial cryptographic transformations. Liu outlined that some measurement standards have already recommended the use of commercial cryptographic algorithms. Regarding processing efficiency, Liu stated that they have addressed concerns through technical validation, demonstrating high efficiency in real-time demasking of 1080P video using only CPU on the Qualcomm 8155 platform without GPU or NPU acceleration. He emphasized the importance of companies conducting relevant tests themselves during compliance work. To facilitate this, they developed a series of tools, including an anonymization testing tool powered by artificial intelligence, which has been adopted by multiple testing agencies for rapid detection of anonymized targets. Liu also discussed the importance of enhancing user experience while ensuring security, advocating for hardware acceleration solutions in communication scenarios, and recommending the use of ECC algorithms for secure startup processes due to their superior speed compared to RSA algorithms. He proposed modular design strategies to lower costs and increase efficiency, suggesting that a single chip could serve multiple applications, such as V2X technology and digital keys. Liu concluded by discussing the potential applications of post-quantum cryptography and AI safety, emphasizing the importance of addressing security vulnerabilities in AI systems.
Beijing Xinchangcheng Technology Discusses Automotive Information Security at Conference

Images

Share this post on: