In the evolution of smart vehicle technology, there are three core development paradigms that reflect not only technological iterations but also different stages of industry logic. Understanding these underlying logics is crucial for grasping the development direction of smart vehicles. The essence of automotive culture can be summarized as 'fixed + stable.' Here, 'fixed' refers to the core matrix of the system remaining unchanged, which directly brings the advantage of stability. Stability is a deep-seated engineering issue on the software level, involving the impact of functional changes during iterations on the system, including fluctuations in CPU and GPU loads over time, all of which are elements that need to be strictly controlled in engineering practice.
In the traditional automotive research and development model, input and output signals are relatively fixed. For example, the control logic of electric windows has predictable input signals and results. In this mode, quality control relies more on the rigor of the process, as stable inputs and fixed designs lead to clear expected results, making high-quality delivery easier to achieve. However, as technology evolves into the fields of assisted driving and intelligent cockpits, the situation fundamentally changes. The uncertainty of external environments forces systems to face dynamic inputs, presenting new challenges to stability. For instance, encountering 32 cones may cause stuttering in the system, an issue that does not arise in traditional fixed input modes but becomes an engineering challenge that must be resolved in the era of assisted driving.
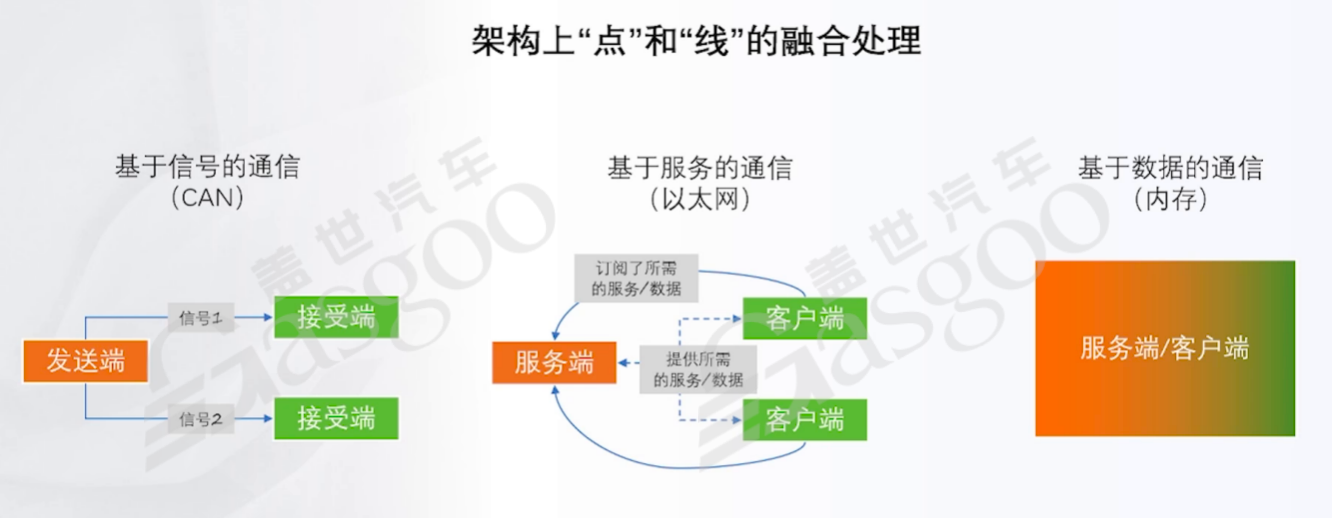
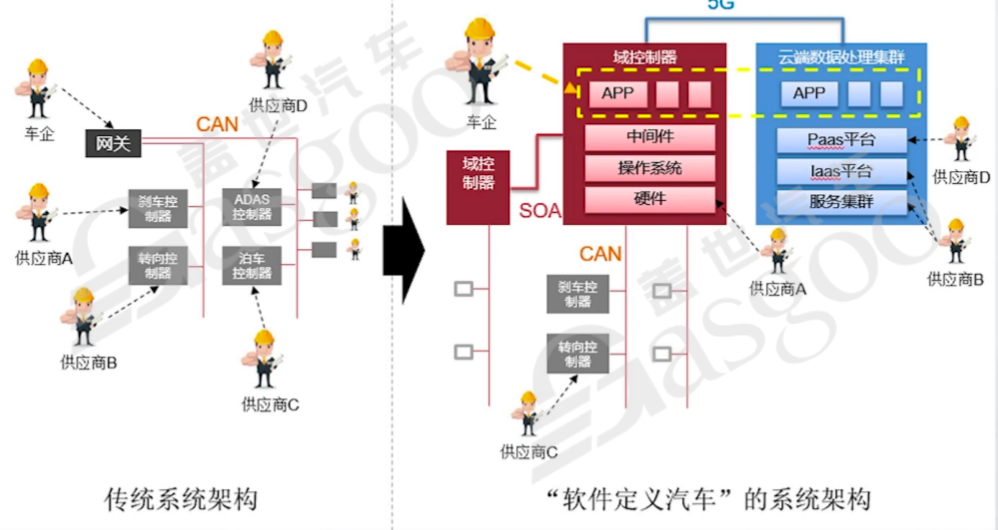
Currently, the industry is in the second paradigm - 'variable + unstable.' With the application of Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA) and the popularization of Firmware Over-The-Air (FOTA) technology, software begins to exhibit variability. Under SOA architecture, communication links between controllers are more flexible, supporting dynamic subscription relationships, theoretically enabling personalized functional customization, such as smoking modes or welcome modes in intelligent cockpits. However, this flexibility comes at the cost of decreased system stability. When multiple controllers subscribe to signals in a disorderly manner, it can lead to a significant increase in server memory usage and even cause software crashes. Even with constraints through version baselines and integration control, the complexity of testing service combinations increases significantly, ultimately resulting in iteration efficiency not improving as expected. This paradox of 'seemingly variable yet needing to be fixed' is the awkward situation currently faced by the industry.
The future third paradigm will be 'variable + stable,' with the core focus on realizing an unmanned system logic. Model-based thinking, represented by GPUs, can maintain stability in computational load when processing dynamic inputs. This means engineering teams do not need to redesign load balancing with each iteration, significantly improving iteration efficiency. For example, an end-to-end model processes varying numbers of obstacles with far less computational load fluctuation than traditional rule-based algorithms, establishing a foundation for rapid iteration. The essence of this paradigm lies in replacing rule-based algorithms with model algorithms to reduce load fluctuations caused by logic adjustments, ultimately achieving the engineering goal of 'stability amidst change.'
The Evolution of Smart Vehicle Development Paradigms and Communication Architectures
Images

Share this post on: